|
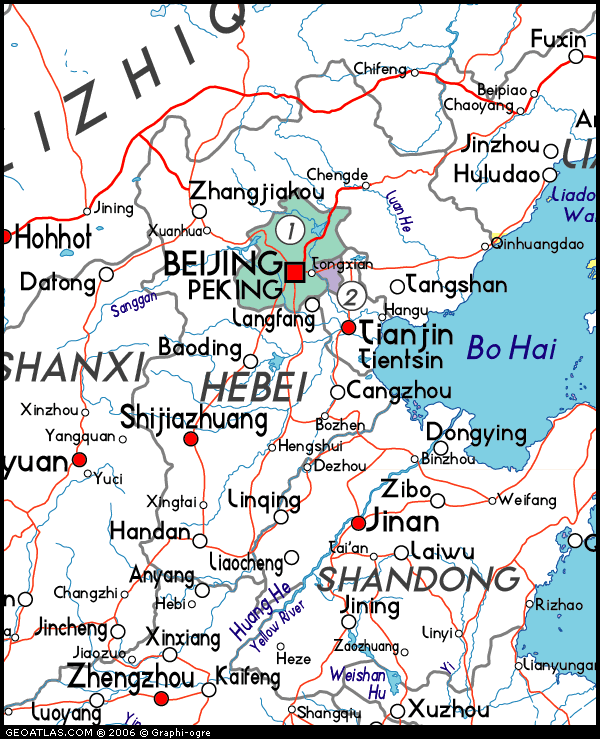
BEIJING Municipality |
|
|
 |
Jietai Temple
戒台寺 |
|
GPS: |
39.8717,
116.08631 |
|
Constructed in the Tang Dynasty
(618-907), covering an area of
11 acres (4 hectares), the
Jietai Temple is a Buddhist
temple in Mentougou District in
western Beijing. It Major
modifications were made during
the Ming and Qing Dynasties. |

 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Badaling Great Wall
八达岭长城 |
|
GPS: |
40.35576,
116.01748 |
|
The Great Wall at Badaling was
completed in 1505 (the 18th year
of the reign of Hong Zhi, an
emperor of the Ming Dynasty).
This section's construction was
led by General Qi Jiguang,
famous for defending China from
Japanese pirates. It is 7.6 km
long. The wall is on average 7.8
meters tall and 5.7 meters wide,
which allowed five horses to
gallop abreast and ten men to
march shoulder to shoulder. |


 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Huanghuacheng Great Wall
黄花城长城 |
|
GPS: |
40.41657,
116.3468 |
|
To enhance the defense of the
northern border, the emperors of
the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644)
built an outer Great Wall and an
inner Great Wall. The
Huanghuacheng section is part of
the inner Great Wall that
connects the Mutianyu section of
the Great Wall in the east, via
Jiankou, and Juyong Pass in the
west. |
 
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Juyongguan
Great Wall
居庸关长城 |
|
GPS: |
40.28941,
116.07624 |
|
The Juyong Pass Great Wall
section was built by the Ming
Dynasty (1368–1644) in this
strategic valley that allowed
direct access to Beijing. It was
built during the reign of
Emperor Zhu Yuanzhang
(1368-1398). He was the first
emperor of the Ming Empire, and
he wanted to fend off attacks
from Mongolians who wanted to
recapture the empire. |


 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Wax Museum |
|
GPS: |
na |
|
N/A |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Palace near Badaling |
|
GPS: |
na |
|
T. |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Tanzhe temple
潭柘寺南口 |
|
GPS: |
39.87027,
116.03853 |
|
The Tanzhe Temple is a Buddhist
temple situated in the Western
Hills, a mountainous area in
western Beijing. At one time, it
was one of the most important
temples in the nation. . It was
originally established in the
Western Jin Dynasty (307 AD). So
far, it has existed for more
than 1,700 years. It is the
first temple built after the
introduction of Buddhism to
Beijing. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Ming Dynasty Tombs
明十三陵 |
|
GPS: |
40.29149,
116.23917 |
|
The Ming tombs are a collection
of mausoleums built by the
emperors of the Ming dynasty of
China. The first Ming emperor's
tomb is located near his capital
Nanjing. However, the majority
of the Ming tombs are located in
a cluster near Beijing and
collectively known as the
Thirteen Tombs of the Ming
Dynasty. |

 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|

|
Changling Tomb
十三陵-长陵 |
|
GPS: |
40.30037,
116.2491 |
|
Changling Tomb, the joint burial
tomb of Emperor Yongle and
Empress Qian, is located in the
southern range of Tianshou
Mountain. Emperor Yongle has
ruled for 22 years, making great
progress in political, economic,
military, cultural and
diplomatic fields. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|

|
Dingling Tomb
明定陵 |
|
GPS: |
40.29586,
116.22352 |
|
Construction of Dingling Tomb
started in 1584 and was finished
in 6 years later. In 1620,
Emperor Wanli was buried here
with his two empresses. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|

|
The Sacred Way (God
Road) 神路 |
|
GPS: |
40.25312,
116.22348 |
|
Constructed since 1435, the 7.3
kilometers long Sacred Way is as
a matter of fact the main way
leading to the thirteen imperial
tombs. The way starts from the
stone memorial archway and ends
at the gate of the Chang
Mausoleum. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Pekin Man (Zhoukoudian)
周口店北京人遗址 |
|
GPS: |
39.69008,
115.92985 |
|
Peking Man (Homo erectus
pekinensis, formerly known by
the junior synonym Sinanthropus
pekinensis) is a group of fossil
specimens of Homo erectus, dated
from roughly 750,000 years ago,
discovered in 1929–37 during
excavations at Zhoukoudian (Chou
K'ou-tien) near Beijing (at the
time spelled Peking). |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BEIJING City (City and City
life) |
|
|
 |
Panjiayuan Antique Market
古董市场潘家园 |
|
GPS: |
39.87536,
116.4594 |
|
Panjiayuan Antique Market first
opened its gates in the 1980s,
starting as a humble roadside
hutong market selling small
handicrafts and artwork. Back in
the day, trading art and other
such items was forbidden in
China, so the market operated in
secret, earning it the nickname
Panjiayuan Ghost Market. But as
time passed and the demand for
antiques and crafts grew, so did
the market. The market is open
all week, but the street stalls
are only open on the weekends
and the best time to go is early
on Saturday or Sunday. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Architecture |
|
GPS: |
na |
|
N/A |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Local life |
|
GPS: |
na |
|
N/A |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Road-Trafic |
|
GPS: |
na |
|
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
TV tower- City View
中央广播电视塔 |
|
GPS: |
39.91956,
116.30631 |
China Central Television Tower
was built in 1987. It is 386.5
meters high. It reaches 405
meters plus the lightning rod.
The observation platform is
situated on the 22nd floor with
a height of 238 meters.
It is
the largest open observation
platform among the towers in the
world. It provides a panoramic
view of the Beijing City. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Beijing
West Railway Station
北京西 |
|
GPS: |
39.89483,
116.3211 |
|
Beijing West Railway Station, or
Beijing West for short, was
completed in early 1996. It is
one of three major railway
stations in Beijing. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Beijing Airport
北京首都国际机场 |
|
GPS: |
40.07985,
116.60311 |
|
Beijing Capital International
Airport is the main
international airport serving
Beijing. It is located 32 km
northeast of Beijing's city
centre. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BEIJING City (Entertainment) |
|
|
 |
Beijing
Acrobatic Show 朝阳剧场 |
|
GPS: |
39.92244,
116.46261 |
|
With a history of more than
three thousand years, Chinese
acrobatics has been praised as
“A pearl of Oriental art”. When
watching a Chinese acrobatics
show, you will be strongly
attracted both mentally and
physically. The acrobatic show
is combined on the base of dance
and opera arts, compositions,
stage design, costume, light and
sound. |

 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Peking Opera
京剧 |
|
GPS: |
na |
|
Peking opera, or Beijing opera,
is the most dominant form of
Chinese opera which combines
music, vocal performance, mime,
dance and acrobatics. It arose
in Beijing in the mid-Qing
dynasty and became fully
developed and recognized by the
mid-19th century. |

 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Beijing
Zoo - Pandas
北京动物园 |
|
GPS: |
39.94,
116.33846 |
|
The Beijing Zoo is a zoological
park in Beijing, the capital of
the China. Founded in 1906
during the late Qing dynasty, it
is the oldest zoo in China and
oldest public park in northern
China. The zoo is also a center
of zoological research that
studies and breeds rare animals
from various continents. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BEIJING City (Historical and
Famous Places) |
|
|
 |
Museum of the War of Chinese
People's Resistance Against
Japanese Aggression
中国人民抗日战争纪念馆 |
|
GPS: |
39.85227,
116.2258 |
The
Museum of the War of Chinese
People's Resistance Against
Japanese Aggression or Chinese
People's Anti-Japanese War
Memorial Hall is the most
comprehensive museum in China
about the Second Sino-Japanese
War.
The
Second Sino-Japanese War was a
military conflict between the
Republic of China and the Empire
of Japan from July 7, 1937 to
September 9, 1945. It ended with
the unconditional surrender of
Japan on September 2, 1945. The
museum is located inside the
Wanping Fortress near the Lugou
Bridge (Marco Polo Bridge). It
was opened on the 50th
anniversary of the outbreak of
Second Sino-Japanese War on July
7, 1987. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Beijing Bell tower
钟楼 |
|
GPS: |
39.94239,
116.39588 |
|
The bell tower was first built
in the ninth year of Zhiyuan
(1272 AD) as the central court
of the Wan Ning Temple in the
Yuan Dynasty, but was destroyed
in the war. It was rebuilt with
the Drum Tower in Yongle in the
18th year (1420 AD) of the Ming
Dynasty as a bell tower, but
unfortunately it was destroyed
again. It was reconstructed in
Qianlong in the 10th year (1745
AD) of the Qing Dynasty and was
finished two years later. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Beijing
Drum
tower
鼓楼 |
|
GPS: |
39.94059,
116.39591 |
|
The Drum Tower was built in1272
during the reign of Kublai Khan.
At that time it was known as the
Tower of Orderly Administration.
In 1420, under the Ming Emperor
Yongle, the building was
reconstructed to the east of the
original site and in 1800 under
the Qing Emperor Jiaqing,
large-scale renovations were
carried out. In 1924, the name
of the building was changed to
the Tower of Realizing
Shamefulness. The first level of
the Drum Tower is a solid square
terrace four meters high, 55.6
meters long and 30 meters wide. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Forbidden
city (Palace Museum)
故宫博物院 |
|
GPS: |
39.91634,
116.39715 |
|
The Forbidden City is a palace
complex in central Beijing,
China. It houses the Palace
Museum, and was the former
Chinese imperial palace and
state residence of the Emperor
of China from the Ming dynasty
to the end of the Qing dynasty,
between 1420 and 1924. |

 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Beijing Ancient Observatory
北京古观象台 |
|
GPS: |
39.90758,
116.43471 |
|
The Beijing Ancient Observatory
is a pretelescopic observatory
located in Beijing, China. The
observatory was built in 1442
during the Ming dynasty, and
expanded during the Qing. It
received major reorganization
and many new, more accurate
instruments from Europeans in
1644. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Beijing
City Walls
北京明城墙 |
|
GPS: |
39.90136,
116.43565 |
|
The old Beijing's city gate and
city wall, basically rebuilt in
the Ming Dynasty (1368-1644),
was composed of four cities
including the Forbidden City as
the core, the palace wall in the
periphery, the inner city and
the outer city. The inner city
has nine city gates whereas the
outer city has seven city gates. |

 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Beijing Hutongs
胡同 |
|
GPS: |
39.94104,
116.39122 |
|
The Mongolians captured the
Beijing area in 1215, and in
1271 they started to build their
Yuan Empire (1271–1368). It was
recorded that in the Yuan Empire
a 36-meter-wide road was called
a standard street, a
18-meter-wide one was a small
street, and a 9-meter-wide lane
was named a hutong. In Beijing,
hutongs are alleys formed by
lines of siheyuan, traditional
courtyard residences. Many
neighbourhoods were formed by
joining one siheyuan to another
to form a hutong. |


 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Marco Polo bridge
卢沟桥 |
|
GPS: |
39.85024,
116.21906 |
|
The Lugou Bridge (Marco Polo
Bridge, the bridge was so named
and known to the west owing to
the description of the famous
Italian explorer Marco Polo) is
the oldest existing multi-arched
stone bridge in the Beijing
area. Construction of the
original bridge on this site
commenced in 1189 and ended in
1192 and was later reconstructed
in 1698. The Lugou Bridge is
266.5 meters in length and 9.3
meters in width, supported on 11
piers. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Beijing
Summer palace
颐和园 |
|
GPS: |
39.99998,
116.27546 |
|
ZThe Summer Palace in Beijing
integrates numerous traditional
halls and pavilions into the
Imperial Garden conceived by the
Qing emperor Qianlong between
1750 and 1764 as the Garden of
Clear Ripples. It covers an area
of 2.9 square kilometres,
three-quarters of which is
water. |

 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Tiananmen
square 天安门广场 |
|
GPS: |
39.90548,
116.39763 |
Tiananmen Square, literally the
"Gate of Heavenly Peace" Square,
covers about 40.5 hectares (100
acres), making it one of the
largest open-air squares in the
world.
Tiananmen gate was first built
in the 1420s during the early
Ming Dynasty. Tiananmen gate
served as the first point of
access to the various gates
leading into the Forbidden City
to the north. When the Qing army
unseated the Ming Dynasty in the
1650s, a detachment of Qing
soldiers damaged or destroyed
the original gate.It was
reconstructed in 1651. |

 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BEIJING City (Parks and
Gardens) |
|
|
 |
Behai
park 北海公园 |
|
GPS: |
39.92544,
116.38926 |
|
Beihai Park, also known as the
Winter Palace, is a public park
and former imperial garden
located in the northwestern part
of the Imperial City, Beijing.
First built in the 11th century,
it is among the largest of all
Chinese gardens and contains
numerous historically important
structures, palaces, and
temples. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Singing Birds |
|
GPS: |
na |
|
N/A |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Jingshan park
景山公园 |
|
GPS: |
39.92509,
116.39684 |
|
Jingshan (literally "Prospect
Hill," also known as Coal Hill)
Park was a part of the Forbidden
City until the early 1900s when
the walls were pulled down and a
road cut through it, destroying
several gates and buildings
between the park and the rear
entrance of the palace. The site
was a private park reserved for
the use of the emperor in the
Yuan dynasty (1279-1368). During
the Ming dynasty (1368-1644), an
artificial hill with five peaks
was made, utilizing earth
excavated when the moat of the
Imperial Palace was dug. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Lianhuachi park
莲花池公园 |
|
GPS: |
39.89201,
116.31202 |
|
The Lianhuachi Park with an area
of 44.6 hectares (110 acres), is
a modern garden and is
well-known for its splendid
lotus scenery. The park was
built on the site of a place of
historical interest-the Lotus
Pond. The pond is regarded as
the birthplace of the city of
Beijing, and bears a history of
over 3,000 years. The capital of
the Jin Dynasty (1115-1234) was
built to the southwest of the
Lotus Pond in 1153 and the pond
provided most of water for the
capital at that time. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Tiantan Park (Temple of Heaven)
天坛公园 |
|
GPS: |
39.88218,
116.4066 |
The
total area of Temple of Heaven
Park is about 270 hectares (670
acres), but the main buildings
are on a south-north line about
750 meters long in the middle of
the park.
The
most striking building of the
Temple of Heaven is the tall,
circular Hall of Prayer for Good
Harvests, in the north of the
park. In the south of the park
lie the Imperial Vault of Heaven
and Circular Mound Altar. The
areas are connected by a
360-meter long, 4-meter wide
walkway, called Danbi Qiao. |

 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Yuanmingyuan park
圆明园遗址公园 |
|
GPS: |
40.00809,
116.29821 |
|
The Old Summer Palace, known in
Chinese as Yuanming Yuan, and
originally called the Imperial
Gardens, was a complex of
palaces and gardens. It is 8
kilometres northwest of the
walls of the former Imperial
City section of Beijing.
Constructed throughout the 18th
and early 19th centuries, the
Old Summer Palace was the main
imperial residence of Qianlong
Emperor of the Qing dynasty and
his successors. |

 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BEIJING City (Temples and
Religion) |
|
|
 |
Temple
of the
Azure clouds
碧云寺 |
|
GPS: |
39.99809,
116.18965 |
|
The Temple of Azure Clouds or
Biyun Temple, was built in the
14th century (possibly in 1331),
during the Yuan dynasty
(1271–1368) and was expanded in
1748. The temple, which is built
on six different levels over an
elevation of nearly 100 meters,
is known for its fine scenery.
The temple also includes the Sun
Yat-sen Memorial Hall. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
The Eight
Great Temples ( Badachu)
八大处公园 |
|
GPS: |
39.95698,
116.18553 |
The
Badachu is a complex of
monasteries which means "Eight
Great Sites" that refers to the
eight Buddhist temples and
nunneries scattered across the
Cuiwei, Pingpo, and Lushi hills.
Chang'an Temple (长安寺), (Temple
of Eternal Peace).
Lingguang Temple (灵光寺), (Temple
of Divine Light).
Sanshan Nunnery (三山庵), (Nunnery
of Three-hills).
Dabei Temple (大悲寺), (Temple of
Great Mercy).
Longquan Nunnery (龙泉庵), (Nunnery
of Dragon Spring).
Xiangjie Temple (香界寺), Temple of
the Fragrant World).
Baozhu Cave (宝珠洞), (Cave of
Precious Pearl).
Zhengguo Temple (正果寺), (Temple
of Thoroughly Transform.) |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Bell
tower temple |
|
GPS: |
na |
|
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Fragrant Hills
香山公园 |
|
GPS: |
39.99133,
116.19382 |
|
Fragrant Hill was used during
the the Jin Dynasty era, and it
has more 800 years of history.
Today, Fragrant Hill is
described as a famous scenic
spot that has a long history and
a beautiful landscape. It
occupies an area of more than
16,000 square meters. The
highest mountain is called
Censer Peak. It has an altitude
of 557 meters. |

 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Beijing Temple of Confucius
北京孔庙 |
|
GPS: |
39.9469,
116.41461 |
|
The temple in Beijing was built
in 1302, and imperial officials
used it to pay their formal
respects to Confucius until
1911. The compound was enlarged
twice, once during the Ming
dynasty and again during the
Qing; it now occupies roughly
20,000 square meters (220,000 sq
ft). It is the second-largest
Confucian temple in China, after
the one in Confucius's hometown
of Qufu. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Temple of the Moon
月坛 |
|
GPS: |
39.91647,
116.35228 |
|
The Temple of the Moon was built
in 1530 during the Ming Dynasty
for use in ritual sacrifice to
the Moon by the Emperor of
China. The altar and the
surrounding grounds are within a
public park. |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Religious procession |
|
GPS: |
na |
|
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Other
Temple |
|
GPS: |
na |
|
N/A |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Temple of Heaven
天坛公园 |
|
GPS: |
39.88218,
116.4066 |
|
Originally constructed during
the Ming Dynasty in 1420, the
Temple of Heaven was a
sacrificial temple used by
emperors during Ming and Qing
dynasties to appease the
heavens, bring prosperity to the
empire and ensure good crops for
the coming year. Sitting in a
large park, the three main
altars – the iconic Hall of
Prayer for Good Harvests, the
Imperial Vault of Heaven and the
Circular Mound Altar. |

 |
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Lama
Temple
雍和宫 |
|
GPS: |
39.94767,
116.41729 |
|
Beijing Lamasery Temple is
called “Yonghegong” in Chinese
which literally means” Harmony
and Peace”. “Yonghegong” is a
romanization form (pinyin) of
the Chinese characters – 雍和宫
(Lama Temple). Yonghegong Lama
Temple was originally built as
the residence of Emperor
Yongzheng when he was still a
prince. After he came to the
throne (Emperor Yongzheng), he
changed his old residence into a
temporary palace called
“Yonghegong” in 1725. In 1744,
his successor, Emperor Qianlong
turned the palace into a lama
temple. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Temple of
White clouds (Baiyuan Guan)
白云观 |
|
GPS: |
39.9003,
116.34374 |
|
The Baiyuan Guan was first built
in 739, with the name of
Tianchang (天长, meaning
'celestial perpetuity') Taoist
Temple, and it soon became the
most influential Taoist temple
in China. In 1148 during the Jin
Dynasty, it was renamed
Changchun Gong (长春宫, meaning
‘Palace of Eternal Spring’). It
was burned down and rebuilt
several times, and most of the
buildings we can see now were
built in the Ming (1368–1644)
and Qing (1644–1911) dynasties. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|